Thinking YOOX: Design Thinking
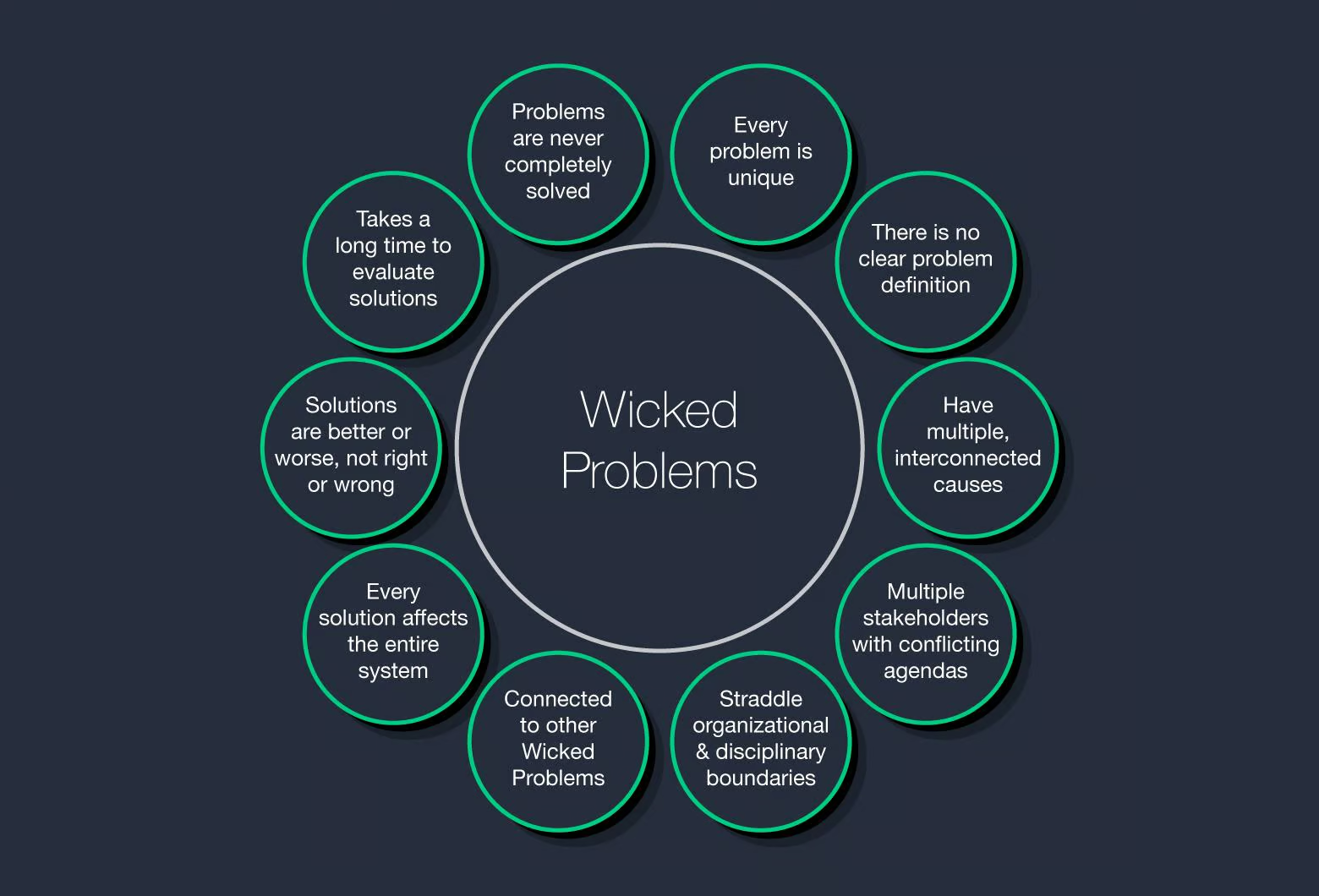
“Design thinking is at the heart of my UX process. I follow a structured, five-phase approach: Product Definition → Research → Analysis → Design → Validation. Each phase ensures that the solutions I design are user-centered, actionable, and aligned with business goals.“
YOOX Space Studio
1. Product Definition:
Before designing, I work with stakeholders to define the product’s purpose and value proposition. This involves:
-
Stakeholder interviews to align on goals.
-
Concept sketching to visualize early ideas.
-
Mapping the user and business needs for a clear foundation.
2. Product research.
I dive into user and market research to understand context, challenges, and opportunities. Techniques include:
-
In-depth interviews (IDIs) to uncover user motivations and pain points.
-
Competitive research to identify industry standards and gaps.
3. Analysis
Research insights are transformed into actionable design direction:
-
Creating user personas representing target audiences.
-
Writing user stories to map needs to product features.
-
Using storyboards to visualize user interactions.
4. Design:
With insights in hand, I iterate on solutions through collaborative and iterative design:
-
Sketches and wireframes for structure and layout.
-
Interactive prototypes to test interactions and flows.
-
Design specifications and systems to ensure consistency and smooth handoff to developers.
5. Validation:
I test early and often to ensure designs meet user needs:
-
Internal testing (“eat your own dogfood”) to catch major issues.
-
User testing sessions with target audiences.
-
Surveys and analytics to capture qualitative and quantitative feedback.
“Design thinking isn’t just a process—it’s about understanding users deeply, iterating continuously, and validating every step of the way.”